Project Brief
Real estate teams receive high volumes of repetitive enquiries across listings, inspections, applications, and property management requests. Customers want instant answers, while agents need only the highest-intent leads routed to them with context.
This project delivered an AI chatbot designed to:
- Answer listing and suburb questions instantly
- Qualify buyer, seller, and tenant intent
- Book inspections and callbacks
- Capture documents and application requirements
- Route complex cases to the right team with full conversation context
client Type
Mid-sized real estate agency group with:
- Sales team (buyers and sellers)
- Leasing team (tenants and applications)
- Property management (maintenance and ongoing requests)
- Existing CRM and listing platforms
My Role
-Conversation design and UX architecture
-Information hierarchy
-intent mapping
-Prototyping and UI design for the chat interface
-Collaboration with AI engineers for prompt and retrieval strategy
-Usability testing, iteration, and handover specs
The Problem
The problem that customers faced :
-Call during business hours
-Fill long forms with unclear outcomes
-Repeat details across multiple teams
The problem that Teams faced :
-Manually answer repetitive questions
-Chase missing details
-Lose leads due to slow response and poor routin
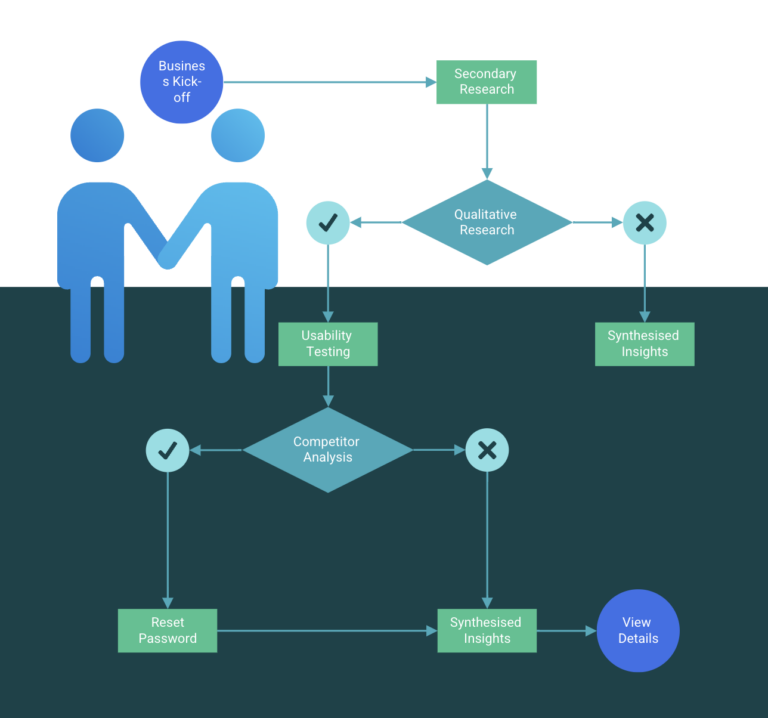
1.1. Insight-to-Strategy Synthesis Map
I. Discovery phase
The 1st phase of the project focused on understanding the problem space for introducing an AI-powered chatbot within a real estate context. This involved aligning with key business stakeholders through a kick-off workshop to understand existing enquiry workflows, operational constraints, and desired business outcomes. The session helped identify success metrics for the chatbot, define scope boundaries, and align assumptions around automation, human handover, and compliance requirements.
Key user groups were identified early in the process, including prospective buyers, sellers seeking property appraisals, rental applicants, existing tenants, sales agents, leasing agents, and property managers. Mapping these groups allowed us to understand differing motivations, information needs, and pain points across the end-to-end real estate journey.
A human-centred design thinking methodology was employed, with end users positioned at the core of the project. The research phase began with secondary research, including analysis of historical enquiry logs, website form submissions, call centre transcripts, CRM data, and property listing analytics. This provided a clear view of the most frequent and high-impact customer enquiries that could be addressed through conversational AI.
Qualitative research was conducted in two stages. The first stage consisted of one-on-one interviews with internal stakeholders and customer-facing staff, including sales agents, leasing consultants, and property managers. These interviews helped uncover behavioural insights around how enquiries are currently handled, where delays occur, and which interactions require human judgment versus automation.
The 2nd stage involved moderated usability testing using early conversational prototypes. Participants were asked to complete common real estate tasks such as enquiring about a property, booking an inspection, requesting an appraisal, and submitting a maintenance request. Screen and conversation flows were recorded and analysed to observe user behaviour, language patterns, hesitation points, and mental models when interacting with an AI-driven interface. These sessions provided valuable insight into how users perceive trust, clarity, and control within a chatbot experience.
In parallel, I conducted a competitor and market analysis across real estate platforms and conversational interfaces used within adjacent industries such as property portals, banking, and customer support automation tools. This analysis focused on conversation structure, escalation patterns, tone of voice, and limitations in existing solutions, helping identify opportunities for differentiation and improvement.
All research findings and key insights were synthesised and documented, then shared with stakeholders to validate assumptions, align on priorities, and inform the next phase of experience design.
1.2. Insight-to-Strategy Synthesis Map

II. Define & Conversation Architecture
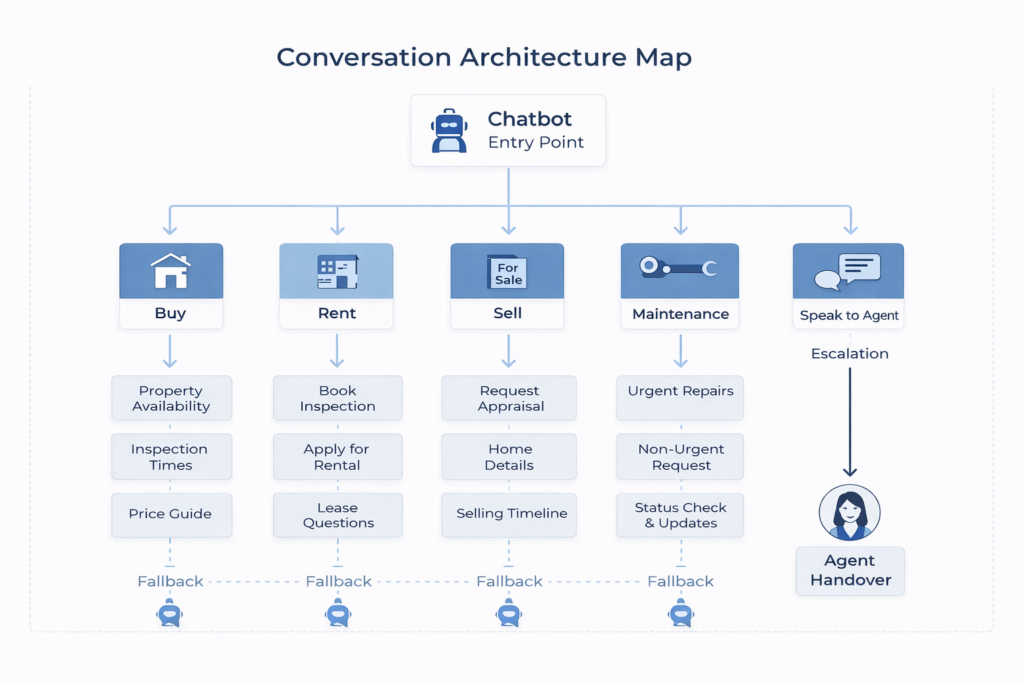
1.3. Conversation Architecture Map
The define phase focused on synthesising insights gathered during discovery and translating them into a clear experience strategy for the AI chatbot. All qualitative and quantitative research findings were analysed and clustered to identify recurring patterns, behavioural pain points, and high-value opportunities for automation within the real estate journey.
Key insights were mapped against business objectives to ensure the chatbot would deliver value to both end users and internal teams. This helped prioritise which interactions should be automated, which required human intervention, and where a hybrid approach would best support trust and decision-making.
Based on this synthesis, I defined a clear set of problem statements and “How Might We” questions that guided the design direction. These focused on reducing response time for high-volume enquiries, improving lead qualification quality, minimising repetitive manual work for agents, and creating a conversational experience that felt reliable, transparent, and easy to navigate.
User Persona & Journey Maps
Primary user personas were then developed for each major journey, including buyers, sellers, rental applicants, existing tenants, and internal real estate staff. Each persona captured user goals, motivations, anxieties, and decision triggers, with particular emphasis on moments of uncertainty where users typically abandon or escalate enquiries. These personas ensured that the chatbot experience was grounded in real user needs rather than technical capabilities alone.
Following this, I mapped end-to-end conversational journeys for each user group. These journeys documented user intents, system responses, decision points, fallbacks, and escalation paths. Special attention was given to identifying critical moments where users required reassurance, clarity, or confirmation, such as booking inspections, requesting property appraisals, or reporting urgent maintenance issues.
I then defined the chatbot’s functional scope and conversation architecture. This included:
Core intents and sub-intents
Entry points across web and mobile platforms
Rules for intent recognition and confidence thresholds
Escalation criteria to human agents
Error handling and recovery paths
To support consistency and scalability, I established conversational design principles covering tone of voice, response length, confirmation patterns, and transparency cues. These principles ensured the chatbot communicated clearly, avoided over-automation, and maintained user trust, particularly in high-stakes real estate interactions.
The define phase concluded with a validated experience blueprint outlining the chatbot’s role within the broader real estate ecosystem. This blueprint was reviewed and signed off by stakeholders and served as the foundation for detailed conversation design, UI prototyping, and technical implementation in subsequent phases.
III. Conversation Design & UX Architecture
Designing the experience strategy
The design phase focused on translating the defined experience strategy into a detailed conversational UX architecture and interface design for the AI chatbot. The primary objective was to create a scalable, intuitive, and trustworthy conversational experience that could support multiple real estate journeys while remaining easy to navigate for users with varying levels of digital confidence.
I began by designing the high-level conversation architecture, mapping primary intents, sub-intents, decision points, and fallback paths for each user group. These flows detailed how users would enter the chatbot, how intent would be identified, how the system would respond, and when escalation to a human agent would be required. Particular attention was given to ensuring users could move forward confidently without feeling trapped in a linear or overly scripted conversation.
Detailed conversation flows were then created for key scenarios, including buyer enquiries, inspection bookings, seller appraisal requests, rental application support, and maintenance requests. Each flow was designed using progressive disclosure, asking only the minimum information required at each step and adapting responses based on user input. This helped reduce cognitive load and mirrored natural human conversation patterns.
Alongside conversation design, I established the chatbot’s tone of voice and interaction principles. The chatbot was designed to communicate clearly, confidently, and transparently, acknowledging uncertainty when required and offering users explicit choices at critical decision points. Trust cues such as confirmation messages, summaries, and optional human handover were intentionally built into the experience.
UI design work focused on creating a clean, accessible chat interface across desktop and mobile. I designed reusable UI components including quick reply buttons, information cards, booking modules, document upload states, and human handover indicators. These components ensured consistency across conversations while allowing flexibility for future expansion of chatbot capabilities.
The design phase concluded with high-fidelity conversational and UI designs, supported by clear interaction guidelines and annotated flows, ready for prototyping and validation.
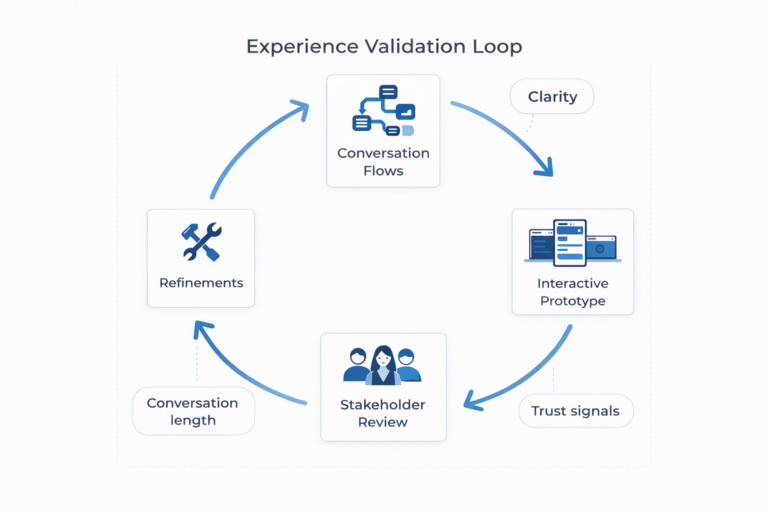
1.4. Experience Validation Loop
IV. Prototyping & UI Design
Low/high fidelity prototyping and usability testing
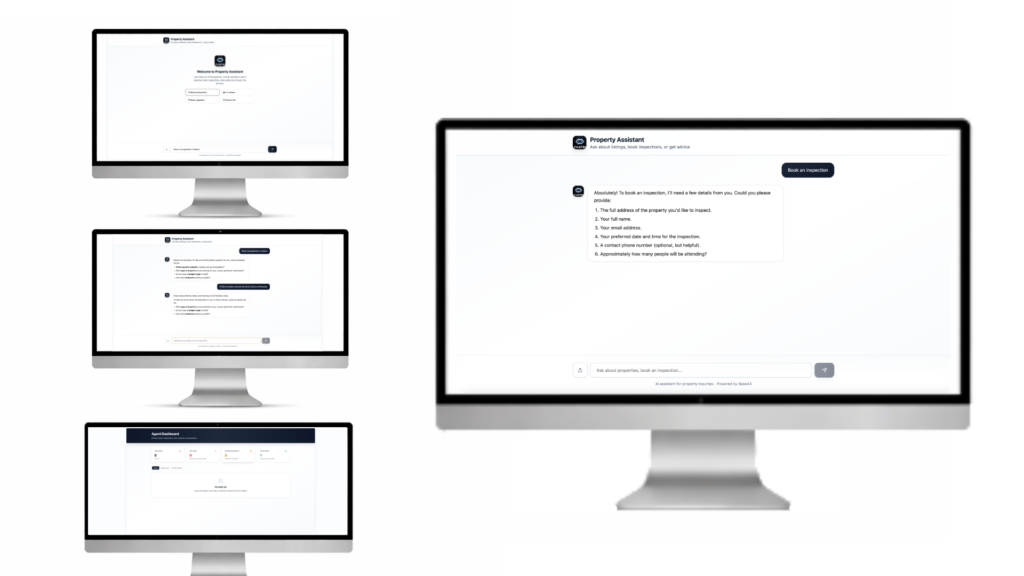
During the prototyping phase, I translated the conversation flows and UI designs into interactive prototypes to validate usability, clarity, and overall experience quality. Prototypes were created to simulate realistic chatbot interactions across key real estate use cases, allowing stakeholders and users to experience the conversation as it would function in a live environment.
I developed clickable and conversational prototypes that demonstrated:
Intent recognition and branching paths
Context-aware responses
Inspection booking flows
Lead qualification summaries
Escalation to human agents
These prototypes enabled early validation of conversation length, question sequencing, response clarity, and user confidence throughout the interaction. Special attention was given to error states, unclear inputs, and edge cases, ensuring the chatbot could recover gracefully and guide users back on track.
Prototypes were shared with cross-functional stakeholders, including product, engineering, and operational teams, to align on feasibility and technical constraints. Feedback from these sessions informed refinements to both the conversation logic and UI patterns before moving into formal testing.
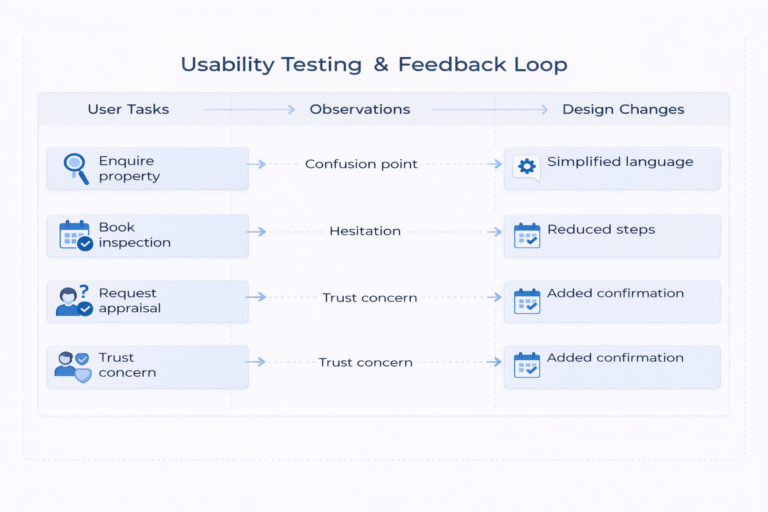
1.5. Usability Testing & Feedback Loop
V. Testing, Iteration & Outcomes
Usability testing was conducted to evaluate how real users interacted with the chatbot and to identify areas of friction or confusion. Moderated usability sessions were run with participants representing buyers, sellers, renters, and existing tenants.
Participants were asked to complete realistic tasks such as enquiring about a property, booking an inspection, requesting a property appraisal, and submitting a maintenance request. Sessions were screen-recorded and analysed to observe user behaviour, language patterns, hesitation points, and emotional responses throughout the conversation.
Insights from testing highlighted opportunities to simplify language, reduce the number of questions in certain flows, and improve visibility of key actions such as booking confirmations and human handover options. Based on these findings, I iterated on conversation flows, refined response phrasing, adjusted UI components, and improved fallback handling.
Multiple iterations were tested to ensure improvements resulted in faster task completion, higher confidence, and reduced drop-off rates. Findings and recommendations were documented and shared with stakeholders to support informed decision-making prior to launch.
1.6. Chatbot prototype
VI. Build & Handover Phase
1.7. Build and handover phase
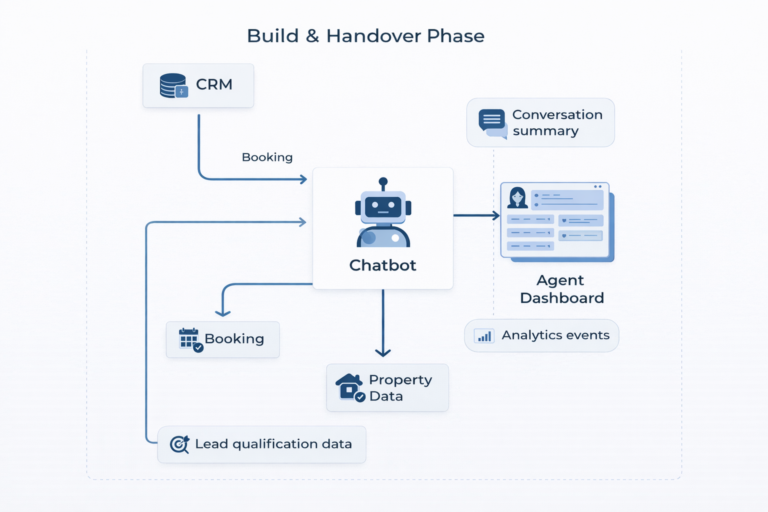
Following validation, I worked closely with engineering teams to support implementation of the chatbot experience. This included providing detailed handover documentation covering conversation logic, intent definitions, escalation rules, UI component specifications, and analytics requirements.
I collaborated with engineers on defining how the chatbot would integrate with existing systems such as CRM platforms, booking tools, and property management workflows. Clear guidance was provided on how conversation summaries and lead data should be structured to ensure agents received meaningful context when a handover occurred.
To support ongoing optimisation, I defined key analytics and success metrics, including intent completion rates, booking conversions, escalation frequency, and post-interaction satisfaction scores. These metrics enabled continuous monitoring and improvement of the chatbot experience post-launch.
VII. Outcome & Impact
The AI chatbot successfully reduced response times for high-volume enquiries while improving lead qualification and operational efficiency for internal teams. Customers were able to access information instantly, book inspections with ease, and understand next steps without needing to call or email.
From a business perspective, the chatbot reduced manual workload for agents, improved data quality within the CRM, and created a consistent, scalable entry point for customer interactions across the real estate journey.